Wisdom Teeth Removal
Introduction to Wisdom Teeth Removal
What is Wisdom Teeth Removal?
Wisdom teeth Removal is a surgical procedure to extract one or more wisdom teeth that are causing pain, crowding, or infection. Since these molars are located at the back of the mouth, they can be difficult to clean and are more prone to cavities and gum disease. The removal process may involve simple extraction or surgical extraction, depending on the tooth’s position and condition.
Talk to our Specialist
What Problems Can Wisdom Teeth Cause?
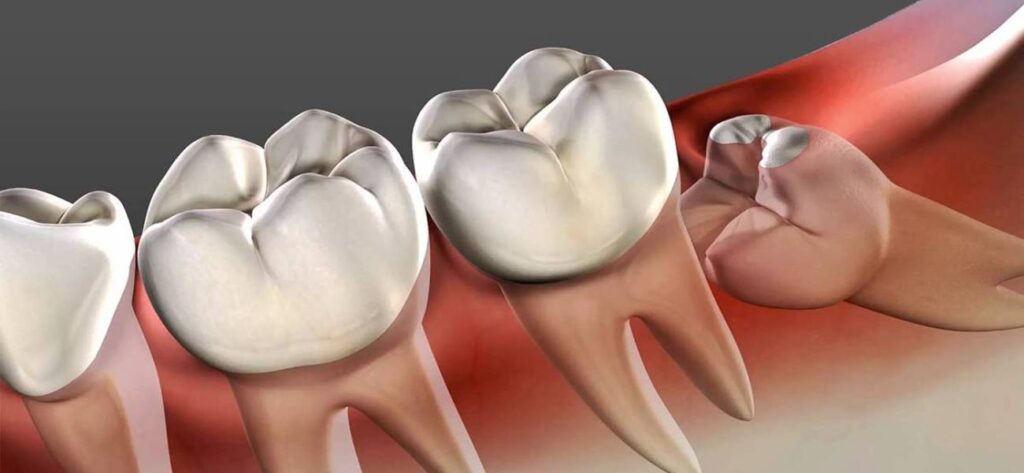
– Impaction: When the tooth is trapped under the gum or in the jawbone, causing pain and swelling.
– Crowding: Wisdom teeth can push against neighbouring teeth, leading to misalignment.
– Infection & Decay: Partially erupted wisdom teeth are difficult to clean, increasing the risk of infection and cavities.
– Cysts or Tumors: In rare cases, cysts may form around an impacted tooth, potentially damaging the jawbone and adjacent teeth.
Types of Wisdom Teeth Removal
- Simple Extraction: If the tooth has fully erupted, it can be removed easily using forceps under local anesthesia.
- Surgical Extraction: If the tooth is impacted, a small incision is made in the gum, and sometimes bone removal is required to extract the tooth. This procedure is done under local or general anesthesia.
Procedure of Wisdom Teeth Removal
- Examination & X-rays: The dentist takes X-rays to determine the tooth’s position and complexity.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local, sedation, or general anesthesia is given to ensure a pain-free procedure.
- Tooth Extraction: The dentist makes an incision (if necessary) and removes the tooth carefully.
- Cleaning & Stitches: The area is cleaned, and stitches may be placed to aid healing.
- Recovery & Aftercare: Patients are advised to follow post-operative care instructions, including avoiding hard foods and maintaining oral hygiene.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Wisdom Teeth Removal
– Persistent pain or discomfort in the back of the mouth
– Swelling, redness, or tenderness in the gums
– Difficulty opening the mouth or chewing food
– Bad breath or unpleasant taste due to infection
– Shifting or crowding of other teeth